External Scan Operation
An external scan is ideal for ad hoc scenarios, where you may receive a file intended to be replicated to a source datastore. Before loading, you can perform an external scan to ensure the file aligns with existing data standards. The schema of the file must match the target table or file pattern that has already been profiled within Qualytics, allowing you to reuse the quality checks to identify any issues before data integration.
Let’s get started 🚀
Navigation to External Scan Operation
Step 1: Select a source datastore from the side menu to perform the external scan operation.
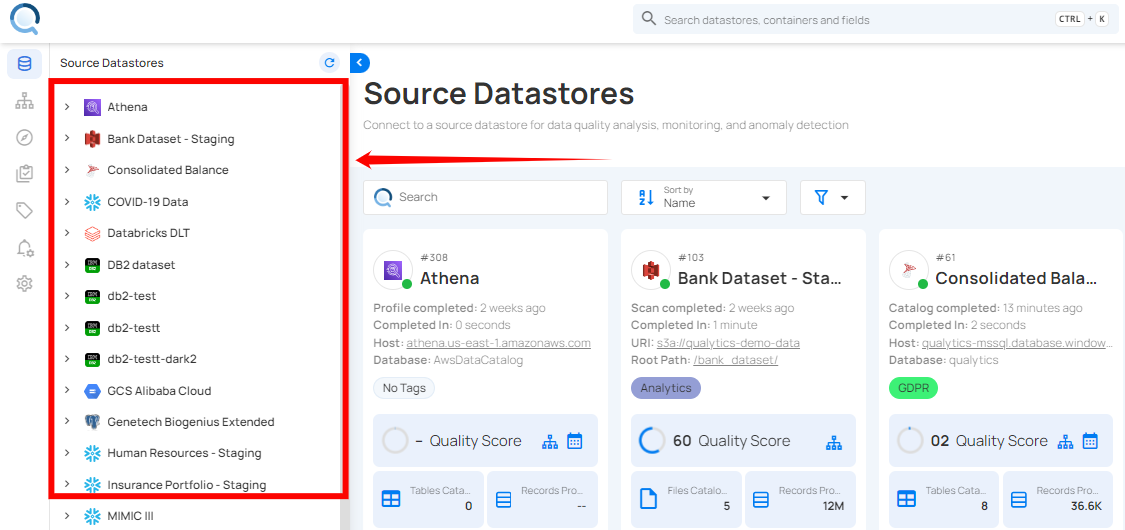
Step 2: After selecting your preferred source datastore, you will be taken to the details page. From there, click on "Tables" and select the table you want to perform the external scan operation on.
Note
This example is based on a JDBC table, but the same steps apply to a DFS as well. For DFS source datastores, you will need to click on "File Patterns" and select a File Pattern to run the external scan.
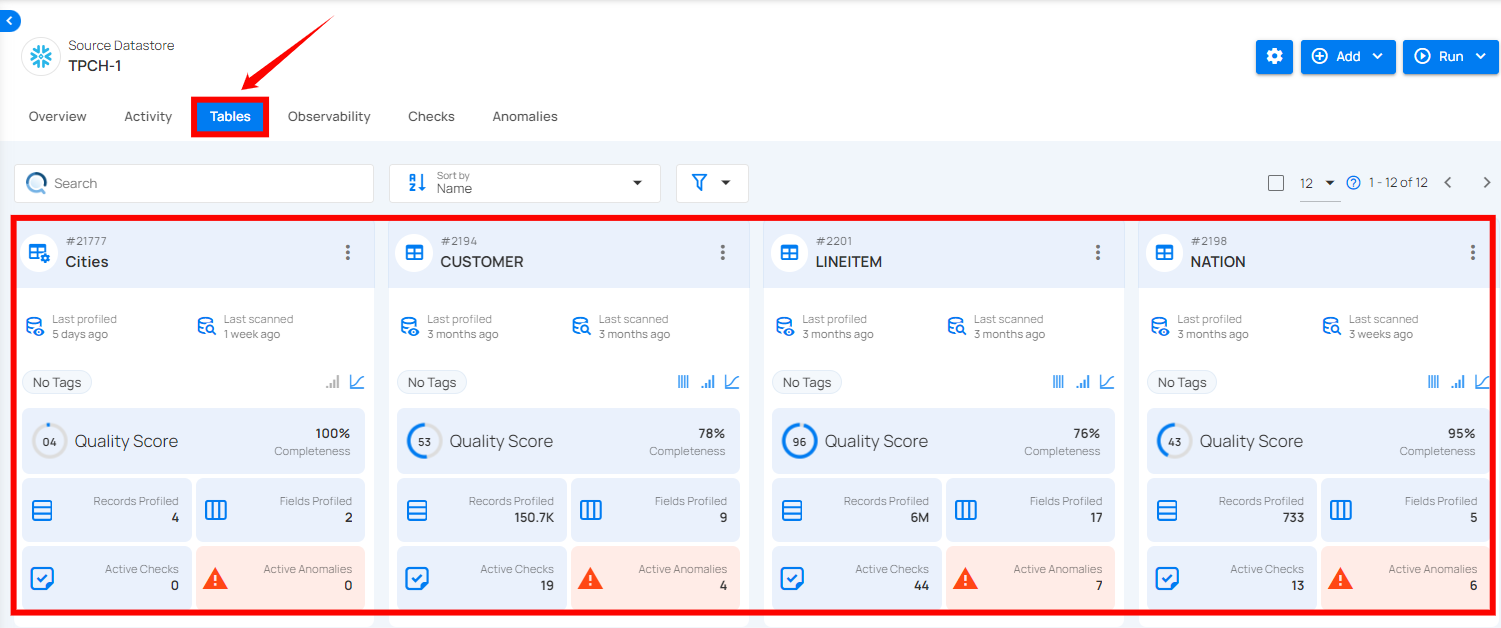
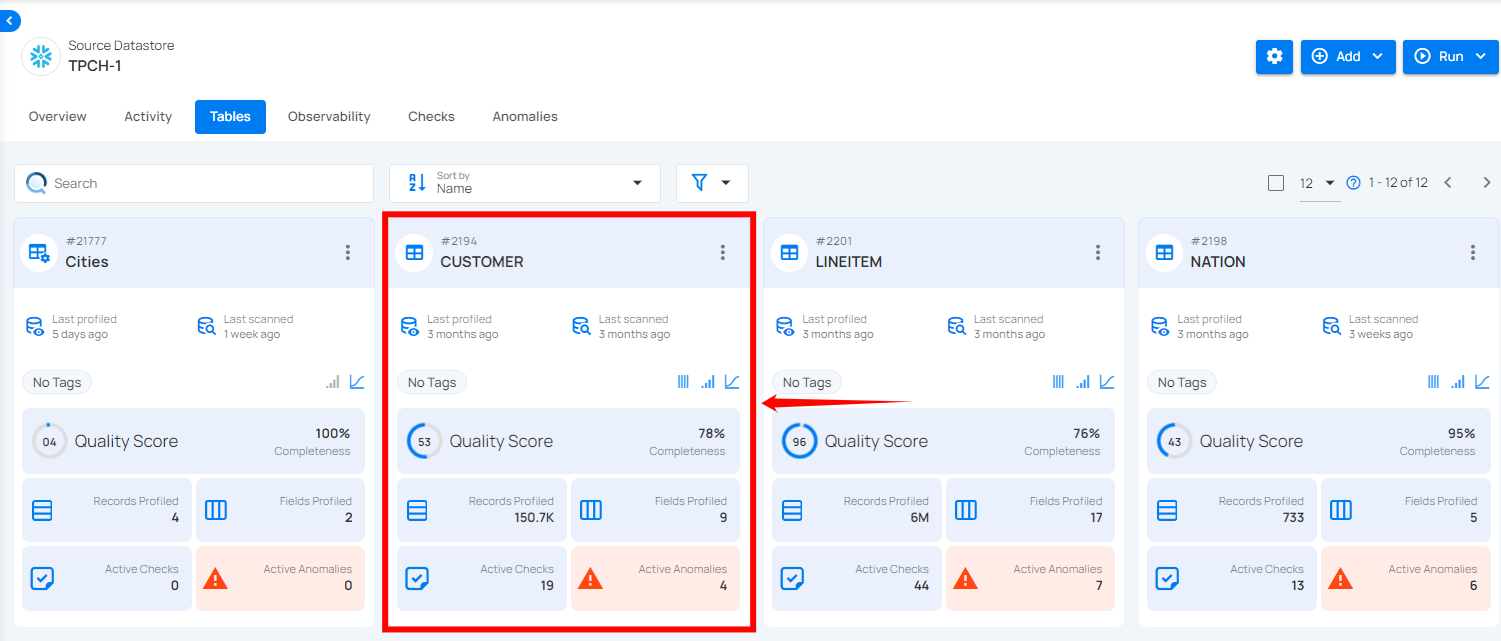
For demonstration purposes, we have selected the “CUSTOMER” table.
External Scan Configuration
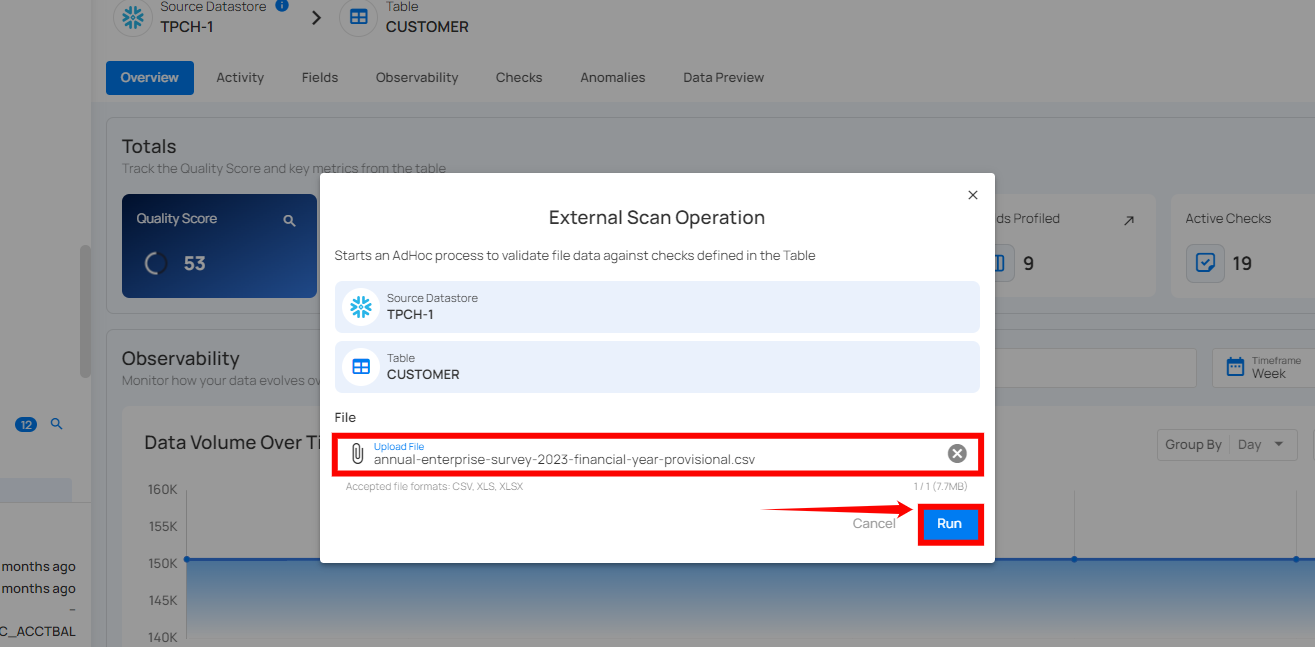
Step 1: Click on the “Run” button and select the “External Scan” option.
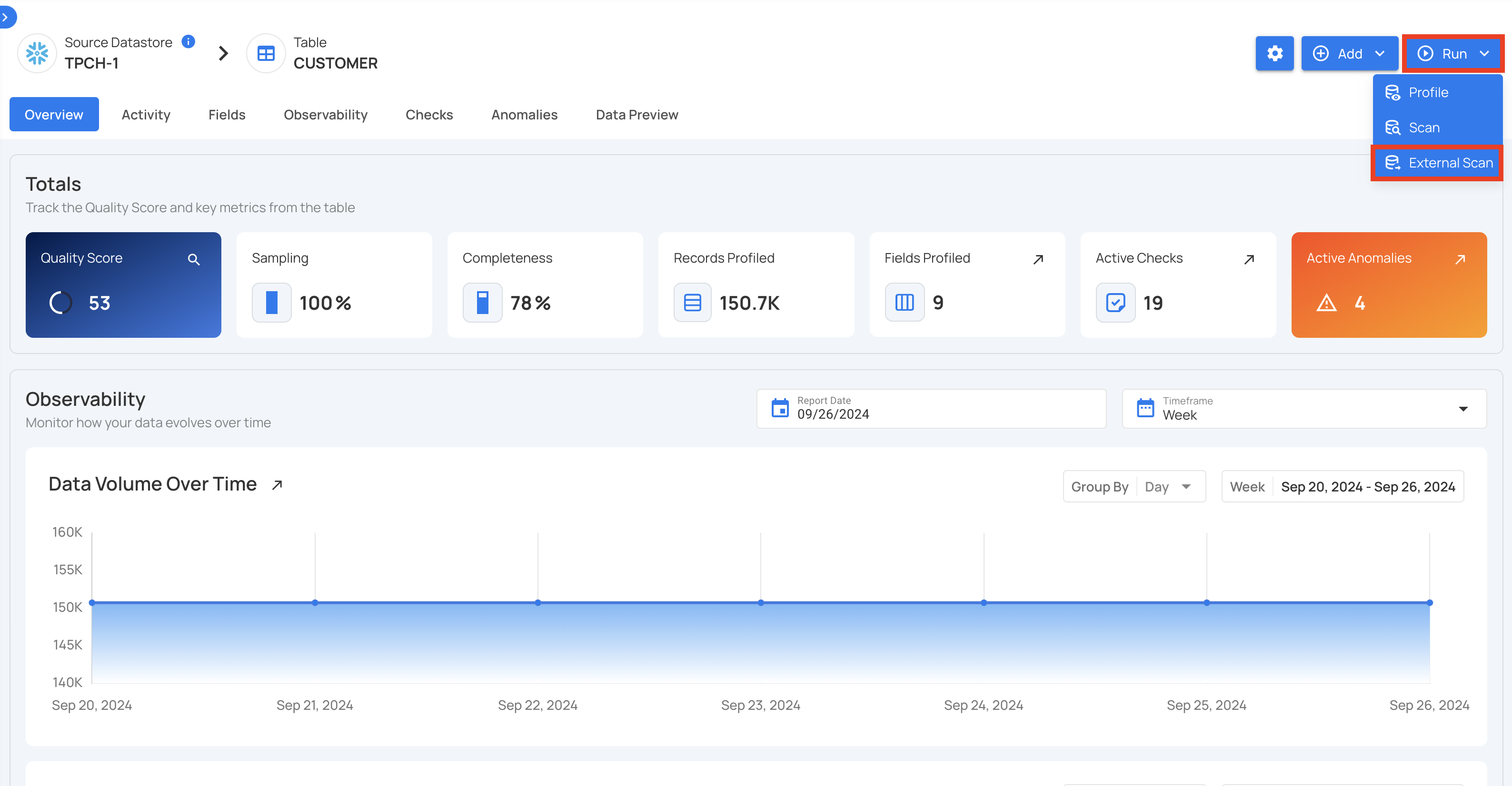
Step 2: After selecting the "External Scan" option, a modal window will appear with an input for uploading your external file. After uploading the file, click the “Run” button to start the operation.
Note
An External Scan operation supports the following file formats: CSV, XLSX, and XLS.
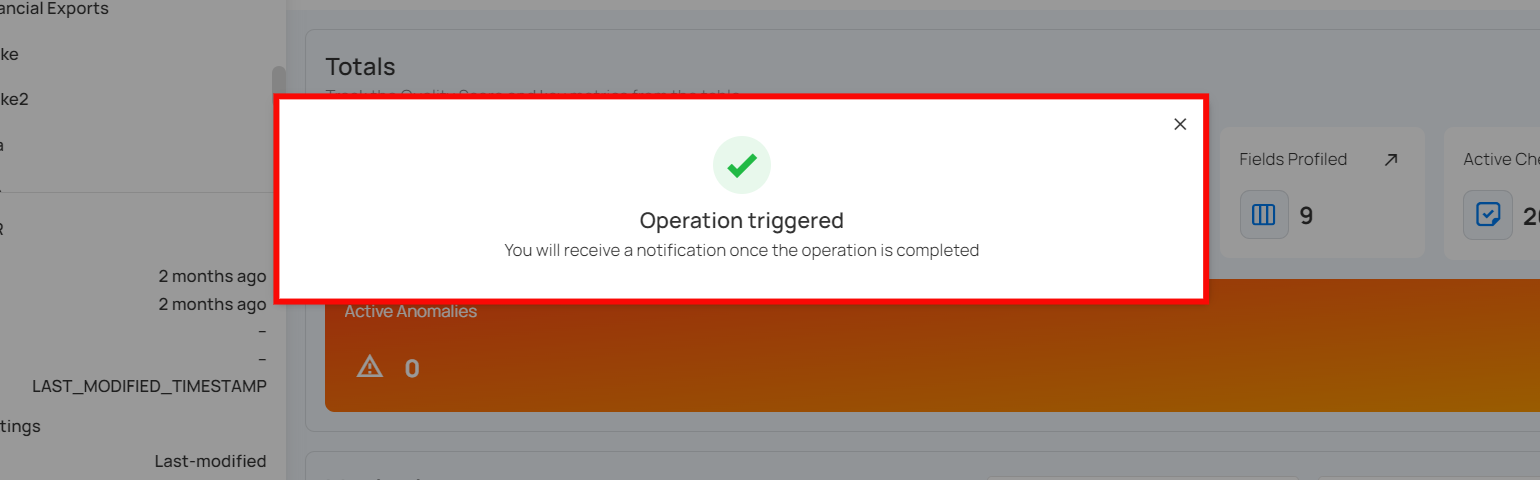
Step 3: After clicking the "Run" button, the external scan operation will begin, and you will receive a confirmation message if the operation is successfully triggered.
Supported File Formats
External scan operation accepts CSV, XLSX, and XLS files. CSV is a simple text format, while XLSX and XLS are Excel formats that support more complex data structures. This versatility enables seamless integration of data from various sources.
An External Scan Operation can be configured with the following file formats:
| File Extension | .csv | .xls | .xlsx |
|---|---|---|---|
| File Format | Comma-separated values | Microsoft Excel 97-2003 Workbook | Microsoft Excel 2007+ Workbook |
| Header Row | Required for optimal reading. It should contain column names. | Recommended, but not strictly required. | Recommended, but not strictly required. |
| Empty Cells | Represented as empty strings. | Allowed. | Allowed. |
| Data Types | Typically inferred by Spark. | May require explicit specification for complex types. | May require explicit specification for complex types. |
| Nested Data | Not directly supported. Consider flattening or using alternative file formats. | Not directly supported. Consider flattening or using alternative file formats. | Not directly supported. Consider flattening or using alternative file formats. |
| Additional Considerations | - Ensure consistent delimiter usage (usually commas). - Avoid special characters or line breaks within fields. - Enclose text fields containing commas or delimiters in double quotes. |
- Use a plain XLS format without macros or formatting. - Consider converting to CSV for simpler handling. |
- Use a plain XLSX format without macros or formatting. - Consider converting to CSV for simpler handling. |
Scenario
A company maintains a large sales database containing information about various transactions, customers, and products. They have received a new sales data file that will be integrated into the existing database. Before loading the data, the organization wants to ensure there are no issues with the file.
An External Scan is initiated to perform checks on the incoming file, validating that it aligns with the quality standards of the sales table.
Specific Checks:
| Check | Description |
|---|---|
Expected Schema |
Verify that all columns have the same data type as the selected profile structure. |
Exists in |
Verify that all transactions have valid customer and product references. |
Between Times |
Ensure that transaction dates fall within an expected range. |
Satisfies Expression |
Validate that the calculated revenue aligns with the unit price and quantity sold. The formula is: R = Quantity × Unit Price |
Potential Anomalies:
This overview highlights common issues such as data type mismatches, missing references, out-of-range dates, and inconsistent revenue calculations. Each anomaly affects data integrity and requires corrective action.
| Anomaly | Description |
|---|---|
| Data type issue | The external resource does not follow the data type schema. |
| Missing References | Transactions without valid customer or product references. |
| Out-of-Range Dates | Transactions with dates outside the expected range. |
| Inconsistent Revenue | Mismatch between calculated revenue and unit price times quantity. |
Benefits of External Scan:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Quality Assurance | Identify and rectify data inconsistencies before downstream processes. |
| Data Integrity | Ensure that all records adhere to defined schema and constraints. |
| Anomaly Detection | Uncover potential issues that might impact business analytics and reporting. |
CSV Table (Sales Data):
This dataset includes transaction records with details such as Transaction_ID, Customer_ID, Product_ID, Transaction_Date, Quantity, and Unit_Price. It provides essential information for tracking and analyzing sales activities.
| Transaction_ID | Customer_ID | Product_ID | Transaction_Date | Quantity | Unit_Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 101 | 201 | 2023-01-15 | 5 | 20.00 |
| 2 | 102 | 202 | 2023-02-20 | 3 | 15.50 |
| 3 | 103 | 201 | 2023-03-10 | 2 | 25.00 |
| 4 | 104 | 203 | 2023-04-05 | 1 | 30.00 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
graph TB
subgraph Init
A[Start] --> B[Load Sales Data]
end
subgraph Checks
B --> C1[Expected schema]
B --> C2[Exists in]
B --> C3[Between times]
B --> C4[Satisfies expression]
C1 -->|Invalid| E1[Expected schema anomaly]
C2 -->|Invalid| E2[Exists in anomaly]
C3 -->|Invalid| E3[Between times anomaly]
C4 -->|Invalid| E4[Satisfies expression anomaly]
end
subgraph End
E1 --> J[Finish]
E2 --> J[Finish]
E3 --> J[Finish]
E4 --> J[Finish]
end
API Payload Examples
Running an External Scan operation
This section provides a sample payload for running an external scan operation. Replace the placeholder values with actual data relevant to your setup.
Endpoint (Post)
/api/containers/{container-id}/scan (post)
Retrieving an External Scan Operation Status
Endpoint (Get)
/api/operations/{id} (get)
{
"items": [
{
"id": 12345,
"created": "YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.ssssssZ",
"type": "external_scan",
"start_time": "YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.ssssssZ",
"end_time": null,
"result": "running",
"message": null,
"triggered_by": "user@example.com",
"datastore": {
"id": 101,
"name": "Datastore-Sample",
"store_type": "jdbc",
"type": "db_type",
"enrich_only": false,
"enrich_container_prefix": "data_prefix",
"favorite": false
},
"schedule": null,
"incremental": false,
"remediation": "none",
"max_records_analyzed_per_partition": -1,
"greater_than_time": null,
"greater_than_batch": null,
"high_count_rollup_threshold": 10,
"enrichment_source_record_limit": 10,
"status": {
"total_containers": 1,
"containers_analyzed": 0,
"partitions_scanned": 0,
"records_processed": 0,
"anomalies_identified": 0
},
"containers": [
{
"id": 234,
"name": "Container1",
"container_type": "table",
"table_type": "table"
}
],
"container_scans": [
{
"id": 456,
"created": "YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.ssssssZ",
"container": {
"id": 234,
"name": "Container1",
"container_type": "table",
"table_type": "table"
},
"start_time": null,
"end_time": null,
"records_processed": 0,
"anomaly_count": 0,
"result": "running",
"message": null
}
],
"tags": []
}
],
"total": 1,
"page": 1,
"size": 50,
"pages": 1
}