Grouping Overview
Grouping is a fundamental aspect of data analysis, allowing users to organize data into meaningful categories for in-depth examination. With the ability to set grouping on Containers, users can define how data within a container should be grouped, facilitating more focused and efficient analysis.
Let’s get started 🚀
Managing an Grouping
Step 1: Log in to your Qualytics account and select the source datastore (JDBC or DFS) from the left menu that you want to manage.
Step 2: Select Tables (if JDBC datastore is connected) or File Patterns (if DFS datastore is connected) from the Navigation tab on the top.
Step 3: You will view the full list of tables or files belonging to the selected source datastore.
Step 4: Click on the vertical ellipse next to the table of your choice and select Settings from the dropdown list.
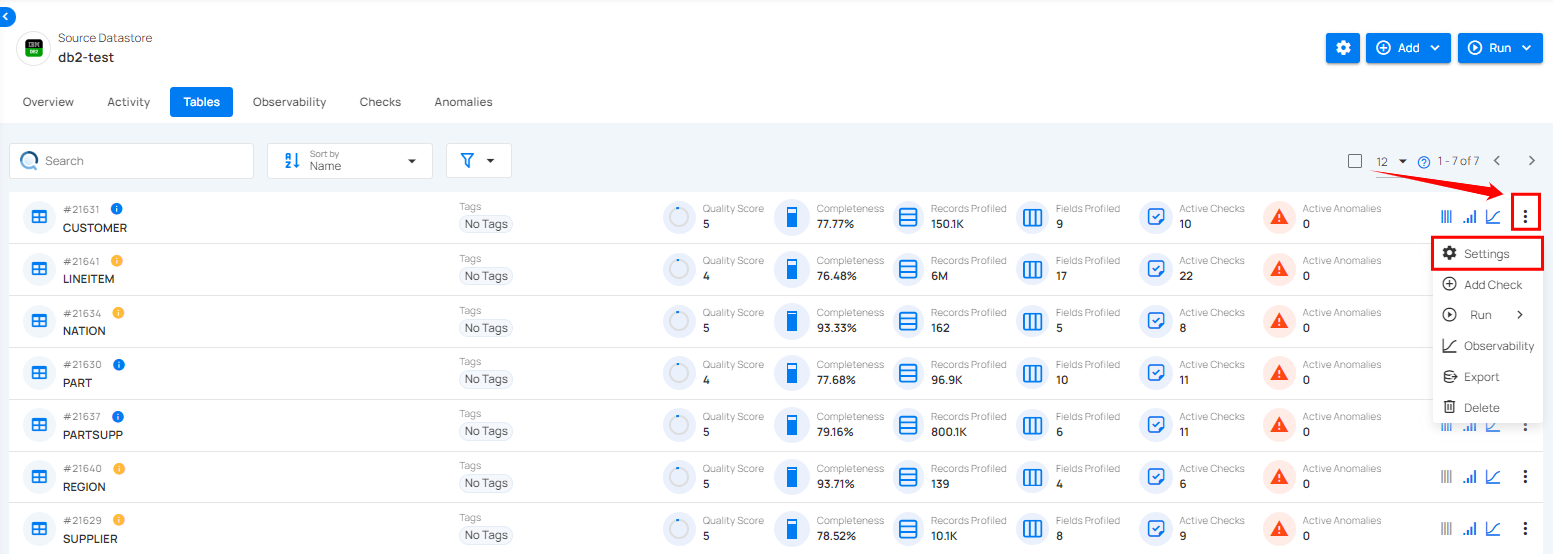
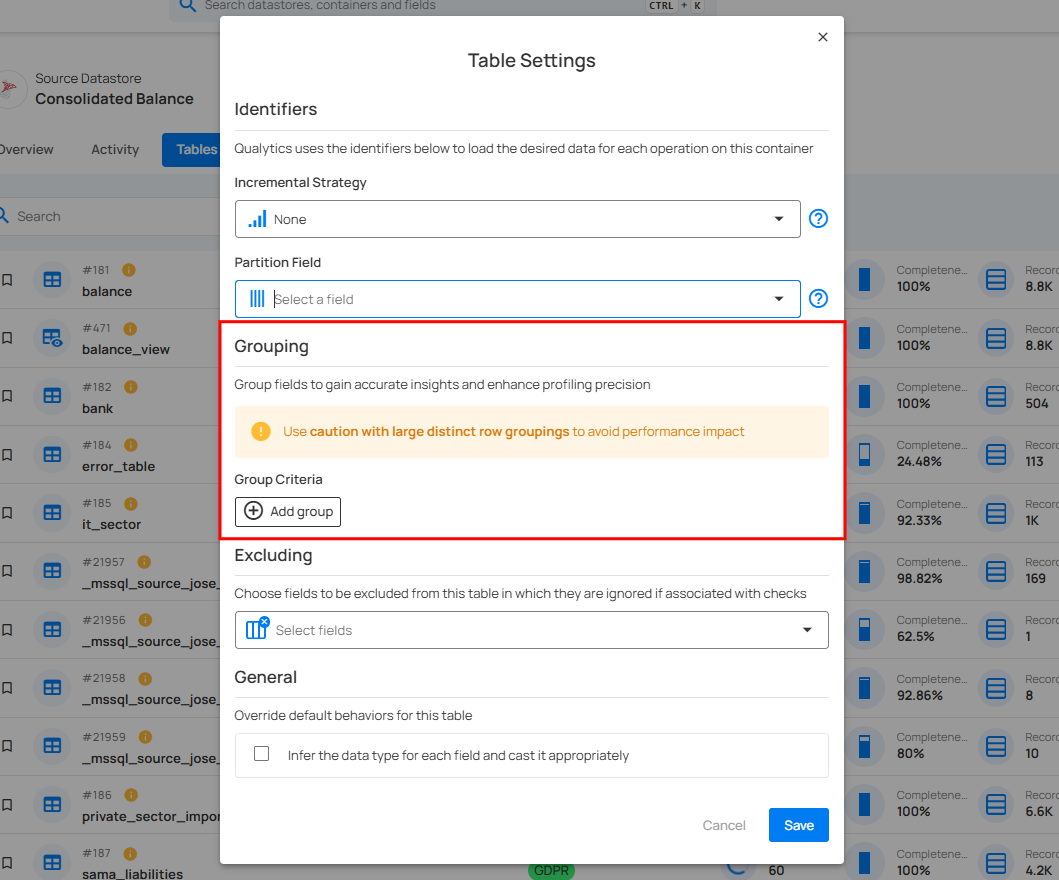
A modal window will appear for “Table Settings”, where you can manage grouping for the selected table.Use the Grouping section to organize fields, with a warning to avoid large row groupings to maintain performance. Add grouping logic via Group Criteria.
Usage
The grouping parameter accepts a list of lists of field names. Each inner list holds the field names in the order that they will be applied as grouping criteria. This flexibility allows users to customize the grouping behavior based on their specific analytical requirements.
Example
Consider the following examples of grouping configurations:
["store_id"]: Groups data within the container by thestore_idfield.["store_id", "month"]: Groups data first bystore_id, then bymonth.["store_id", "state"]: Groups data first bystore_id, then bystate.
By specifying different combinations of fields in the grouping parameter, users can tailor the grouping behavior to suit their analytical needs.
Impact on Data Profiles
The grouping has implications for various aspects of data profiling and analysis within Qualytics.
Field Profiles
Field Profiles are now produced with filters determined by the grouping specified on the Profile Operation. This means that the profiles generated will reflect the characteristics of data within each group defined by the grouping criteria.
Inferred Quality Checks
The inferred checks produced by the analytics engine will also hold the filter defined by the grouping. This ensures that data access controls and constraints are applied consistently across different groupings of data within the container.
Inferred Quality Check Filters
Quality Check filters, represented as Spark SQL where clauses, are set based on the grouping specified on the Profile Operation. This ensures that quality checks are applied appropriately to the data within each group, allowing for comprehensive data validation and quality assurance.
Conclusion
The introduction of Grouping for Containers in Qualytics enhances data organization and analysis capabilities, allowing users to define custom grouping criteria and analyze data at a granular level. By leveraging grouping, users can gain deeper insights into their data and streamline the analytical process, ultimately driving more informed decision-making and improving overall data quality and reliability.